Solar generator for off grid living – Solar generator for off-grid living offers a compelling solution for those seeking energy independence. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of designing and implementing a reliable off-grid solar power system, from selecting the right generator and battery technology to understanding safety regulations and maintenance procedures. We delve into the intricacies of power requirements, system sizing, and panel installation, empowering readers to make informed decisions and achieve sustainable, self-sufficient living.
This guide provides a practical roadmap for navigating the complexities of off-grid power, covering everything from calculating energy needs and choosing appropriate components to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your solar generator system. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY enthusiast or a novice exploring off-grid options, this resource offers valuable insights and practical advice to help you harness the power of the sun and achieve energy freedom.
Solar Generator Types for Off-Grid Living: Solar Generator For Off Grid Living
Choosing the right solar generator is crucial for successful off-grid living. The decision hinges on several factors, including energy needs, budget, and the specific demands of your off-grid location. This section details the various types of solar generators, their characteristics, and the process of selecting the best fit for your needs.
Solar Generator Types: A Comparison
Two primary battery chemistries dominate the off-grid solar generator market: lithium-ion and lead-acid. Each offers distinct advantages and disadvantages concerning lifespan, weight, cost, and energy density.
| Feature | Lithium-ion (LiFePO4) | Lead-Acid (Flooded/AGM) |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan (cycles) | 2000-5000+ | 300-500 |
| Weight (per kWh) | Relatively light | Relatively heavy |
| Cost (per kWh) | Higher | Lower |
| Energy Density | High | Low |
Portable vs. Stationary Solar Generator Systems
The choice between portable and stationary systems depends on your needs and lifestyle. Portable systems offer flexibility, allowing you to easily move them to different locations. Stationary systems, on the other hand, provide a more permanent and often higher-capacity power solution.
- Portable Systems: Ideal for camping, RVs, or temporary off-grid situations. They are generally smaller and lighter, but with lower capacity.
- Stationary Systems: Better suited for permanent off-grid homes. They are larger and heavier, offering significantly higher energy storage capacity.
Solar Generator Selection Flowchart, Solar generator for off grid living
The following flowchart Artikels the decision-making process for choosing the right solar generator.
(A flowchart would be inserted here visually depicting the decision-making process. The flowchart would start with assessing energy needs, then branch to budget considerations, leading to choices between portable and stationary systems, and finally culminating in the selection of specific battery chemistry and system components.)
The rising popularity of off-grid living is fueling demand for reliable solar generators. These systems offer a sustainable energy solution, providing power for essential appliances and devices. For those new to this lifestyle, a great resource for learning more about self-sufficiency is the introductory guide found at Hello world! , which provides a basic framework for understanding the needs of independent living.
Ultimately, the right solar generator ensures consistent power for a comfortable and independent off-grid existence.
Power Requirements and Sizing a Solar Generator System
Accurately assessing your daily energy consumption is the foundation of designing an effective off-grid solar power system. This involves identifying all energy-consuming appliances and calculating their daily energy usage.
Calculating Daily Energy Consumption
To calculate daily energy consumption, list all appliances, their wattage, and their daily usage hours. Multiply wattage by hours of use for each appliance, then sum the results to get the total daily energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh). For example: A 100-watt refrigerator running for 12 hours consumes 1200 Wh (100W x 12h).
Sizing a Solar Generator System
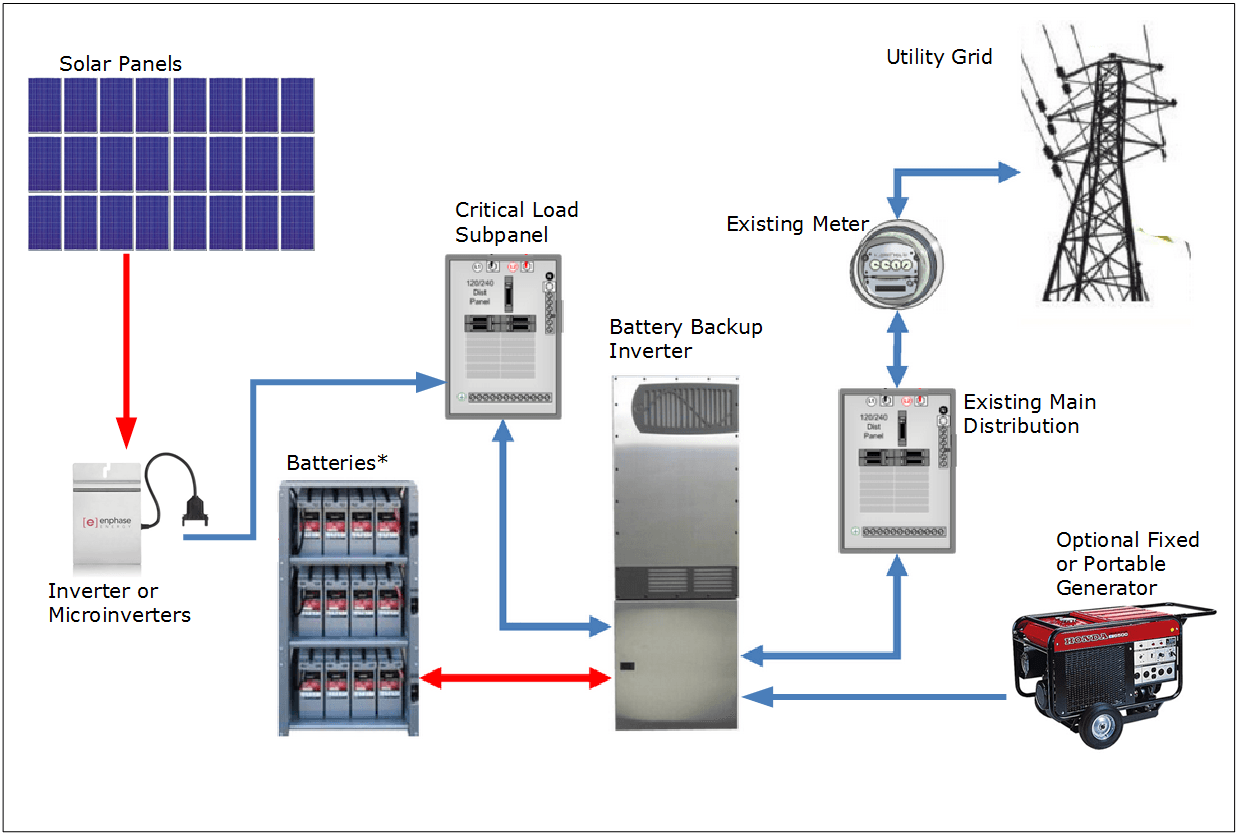
Source: cloudfront.net
Sizing a solar generator involves determining the appropriate solar panel wattage and battery bank capacity to meet your calculated energy needs. Several factors must be considered.
- Daily energy consumption: The total watt-hours needed daily.
- Solar panel efficiency: The percentage of sunlight converted to electricity.
- Battery capacity: The amount of energy the battery can store.
- Inverter efficiency: The efficiency of converting DC power from the batteries to AC power for appliances.
- Days of autonomy: The number of days the system should operate without sunlight.
Determining Solar Panel Wattage and Battery Bank Capacity
- Calculate total daily energy needs: Sum the energy consumption of all appliances.
- Account for system losses: Add 20-30% to the total daily energy needs to account for inefficiencies in the system.
- Determine solar panel wattage: Divide the adjusted daily energy needs by the average daily peak sun hours in your location. This gives you the required solar panel wattage.
- Determine battery bank capacity: Multiply the adjusted daily energy needs by the desired days of autonomy. This determines the minimum battery capacity needed in watt-hours.
Battery Technology and Maintenance
Different battery chemistries offer varying performance characteristics, lifespans, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting and maintaining your off-grid solar power system.
Battery Chemistry Comparison
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) and lead-acid batteries are the most common choices for off-grid systems. LiFePO4 batteries boast superior lifespan, higher energy density, and better performance in extreme temperatures, but they are more expensive. Lead-acid batteries are more affordable but have shorter lifespans and require more maintenance.
Battery Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is essential for extending battery life and ensuring optimal system performance. This includes checking electrolyte levels (for lead-acid batteries), keeping terminals clean, and avoiding deep discharges.
Battery Technology Characteristics
| Feature | LiFePO4 | Lead-Acid (Flooded) | Lead-Acid (AGM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expected Lifespan (cycles) | 2000-5000+ | 300-500 | 500-800 |
| Charging Cycles | High | Low | Medium |
| Maintenance Requirements | Minimal | Regular electrolyte checks | Minimal |
Solar Panel Selection and Installation
Choosing and installing solar panels correctly is critical for system efficiency and safety. This section covers key factors to consider during selection and provides a guide for safe installation.
Solar Panel Selection Factors
When selecting solar panels, consider panel wattage, efficiency, temperature coefficient, and manufacturer reputation. Higher wattage panels generate more power, while higher efficiency panels produce more power per unit area. The temperature coefficient indicates how panel output changes with temperature variations.
Solar Panel Mounting Options
Several mounting options exist, including roof mounts, ground mounts, and portable mounts. The choice depends on your location, roof type, and aesthetic preferences. Roof mounts are common for permanent installations, while ground mounts are suitable for open areas. Portable mounts provide flexibility for moving the panels.
Safe Solar Panel Installation
Safe installation involves adhering to electrical codes, using appropriate wiring and connectors, and employing proper grounding techniques. Always disconnect the system before working on it and use appropriate safety equipment. (A detailed description of safe installation practices, including wiring diagrams and connection procedures, would be included here. Descriptive captions would accompany illustrations of safe installation practices.)
Inverter Selection and Functionality
Inverters convert the DC power from the solar panels and batteries into AC power used by household appliances. Choosing the right inverter is essential for compatibility and system efficiency.
Inverter Types
Pure sine wave inverters provide cleaner power, suitable for sensitive electronics. Modified sine wave inverters are less expensive but may not be compatible with all appliances. The choice depends on the types of appliances you plan to use.
Inverter Sizing
The inverter must be sized to handle the peak power draw of your appliances. Undersizing can lead to overloading and damage, while oversizing increases costs without significant benefit.
Charge Controller Function
Charge controllers regulate the flow of power from the solar panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and extending battery life. They are essential components of any off-grid solar system.
Off-Grid System Design and Integration
Designing a complete off-grid system requires careful planning and consideration of various components. This section provides guidance on system design and integration with other off-grid components.
Off-Grid System Design
A typical off-grid system includes solar panels, a charge controller, a battery bank, and an inverter. The size of each component is determined by your energy needs and budget. (Examples of system schematics and wiring diagrams for different off-grid applications would be included here.)
System Integration
Integrating the solar generator with other off-grid components, such as water pumps and lighting, requires careful planning to ensure compatibility and efficient power distribution. Proper wiring and protection devices are essential.
Safety Precautions and Regulations
Off-grid solar power systems, while beneficial, present potential safety hazards if not handled correctly. This section emphasizes safety precautions and relevant regulations.
Safety Hazards and Mitigation
Potential hazards include electrical shocks, fire hazards, and exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Mitigation strategies include proper grounding, using appropriate safety equipment, and regular system inspections.
Safety Regulations and Building Codes
Adhering to local safety regulations and building codes is crucial for legal compliance and system safety. These regulations often specify wiring requirements, grounding practices, and safety inspections.
Safety Checklist
A comprehensive checklist would be included here, covering safety procedures for installation, operation, and maintenance of off-grid solar systems. This checklist would include pre-installation checks, installation procedures, operational checks, and regular maintenance procedures.
Concluding Remarks
Embarking on off-grid living with a solar generator system requires careful planning and consideration, but the rewards of energy independence are substantial. By understanding the various components, their interplay, and the crucial safety aspects, individuals can create a reliable and sustainable power solution tailored to their specific needs. This guide serves as a valuable resource for anyone venturing into the world of off-grid solar power, offering the knowledge and confidence to build a system that powers a self-sufficient and environmentally conscious lifestyle.
